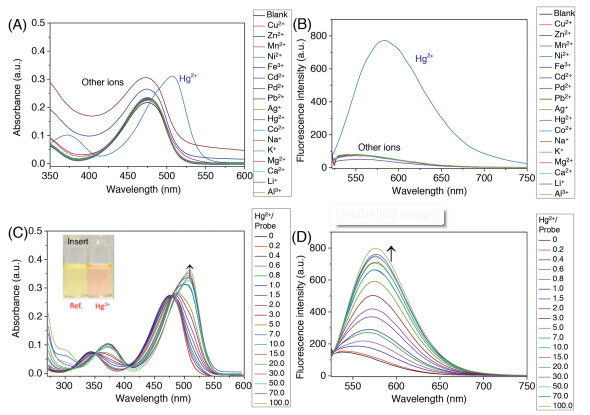
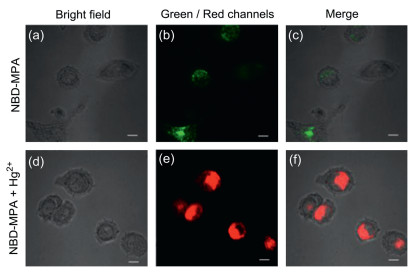
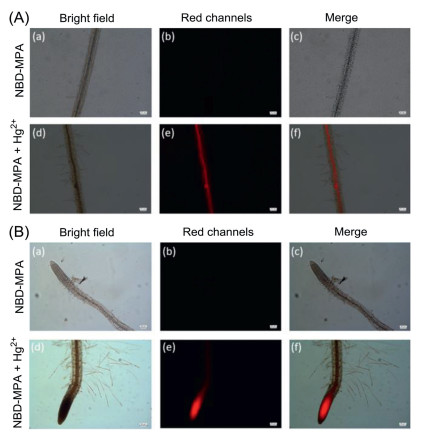
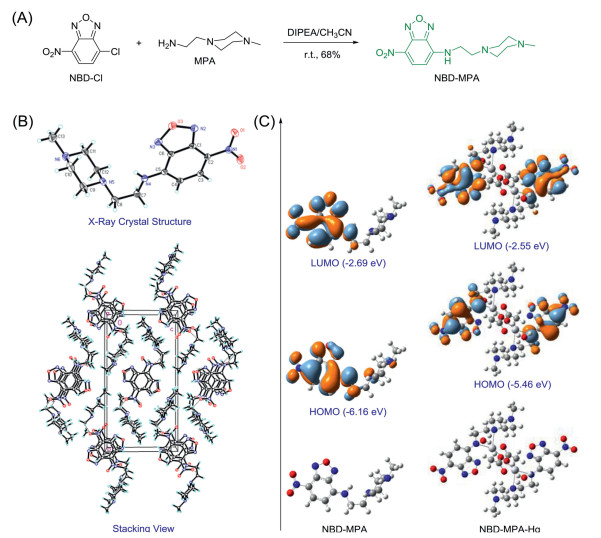
-
[1]
L. Zou, Z. Gu, M. Sun, Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 97 (2015) 477-490.
doi: 10.1080/02772248.2015.1050201
-
[2]
P.A. Nogara, M. Farina, M. Aschner, et al., Chem. Res. Toxicol. 32 (2019) 1459-1461.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.9b00126
-
[3]
Z. Hao, R. Zhu, P. Chen, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 43 (2018) 87-96.
-
[4]
Y. Yang, Q. Zhao, W. Feng, et al., Chem. Rev. 113 (2013) 192-270.
doi: 10.1021/cr2004103
-
[5]
Z. Liang, C. Wang, J. Yang, New J. Chem. 31 (2007) 906-910.
doi: 10.1039/b701201m
-
[6]
B. Yin, B. Ye, W. Tan, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (2009) 14624-14625.
doi: 10.1021/ja9062426
-
[7]
(a) R.A. Sánchez-Moreno, M.J. Gismera, M.T. Sevilla, et al., Phytochem. Anal. 21 (2010) 340-347;
(b) M. Porento, V. Sutinen, T. Julku, et al., Appl. Spectrosc. 65 (2011) 678-683.
-
[8]
A.R. Date, A.E. Davis, Y.Y. Cheung, Analyst 112 (1987) 1217-1222.
-
[9]
E.M. Nolan, S.J. Lippard, Chem. Rev. 108 (2008) 3443-3480.
doi: 10.1021/cr068000q
-
[10]
(a) J.A. Caruso, B. Klaue, B. Michalke, et al., Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 56 (2003) 32-44;
(b) T.T. Shih, W.Y. Tseng, K.H. Tsai, et al., Microchem. J. 99 (2011) 260-266.
-
[11]
(a) S. Saracoglu, M. Soylak, D.K. Peker, et al., Anal. Chim. Acta 575 (2006) 133-137;
(b) Y. Boukraa, D. Barkat, T. Benabdellah, et al., Phys. Chem. Liq. 44 (2006) 693-700.
-
[12]
(a) F. Deng, Z. Xu, Chin. Chem. Lett. 30 (2019) 1667-1681;
(b) D. Wu, L. Chen, W. Lee, et al., Coord. Chem. Rev. 354 (2018) 74-97;
(c) J. Yin, Y. Hu, J. Yoon, Chem. Soc. Rev. 44 (2015) 4619-4644.
-
[13]
(a) L. Yu, Y. Qiao, L. Miao, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 29 (2018) 1545-1559;
(b) H.N. Kim, W.X. Ren, J.S. Kim, et al., Chem. Soc. Rev. 41 (2012) 3210-3244;
(c) P.R. Sahoo, K. Prakash, S. Kumar, Coord. Chem. Rev. 357 (2018) 18-49;
(d) G. Zhu, C. Zhang, Analyst 139 (2014) 6326-6342;
(e) Q. Zhao, F. Li, C. Huang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 39 (2010) 3007-3030;
(f) X. Ma, L. Hu, X. Han, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 29 (2018) 1489-1492;
(g) W. Chen, Y. Pan, J. Chen, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 29 (2018) 1429-1435.
-
[14]
(a) L. Li, Y. Chen, W. Chen, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 30 (2019) 1689-1703;
(b) Y. Chen, L. Li, W. Chen, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 30 (2019) 1353-1360;
(c) H. Xiao, W. Zhang, P. Li, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59 (2020) 4216-4230;
(d) S. Park, N. Kwon, J. Lee, et al., Chem. Soc. Rev. 49 (2020) 143-179;
(e) A. Aliyan, N.P. Cook, A.A. Marti, Chem. Rev. 119 (2019) 11819-11856;
(f) H. Singh, K. Tiwari, R. Tiwari, et al., Chem. Rev. 119 (2019) 11718-11760;
(g) Y. Wen, F. Huo, C. Yin, Chin. Chem. Lett. 30 (2019) 1834-1842;
(h) M. Yang, J. Fan, J. Du, et al., Chem. Sci. 11 (2020) 5127-5141;
(i) W. Chi, Jie Chen, W. Liu, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (2020) 6777-6785.
-
[15]
(a) J. Zhu, P. Jia, N. Li, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 29 (2018) 1445-1450;
(b) Z. Lei, X. Li, X. Luo, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 (2017) 2979-2983;
(c) J. Zhu, X. Liu, J. Huang, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 30 (2019) 1767-1774.
-
[16]
B.A.D. Neto, P.H.P.R. Carvalho, J.R. Correa, Acc. Chem. Res. 48 (2015) 1560-1569.
doi: 10.1021/ar500468p
-
[17]
(a) X. Han, X. Lv, Z. Chen, et al., Chin. J. Chem. 33 (2015) 1064-1068;
(b) G. Li, Y. Guan, F. Ye, et al., Spectrochim. Acta A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 239 (2020);
(c) Y. Zhang, H. Chen, D. Chen, et al., Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 224 (2016) 907-914;
(d) S. Oh, J. Jeon, J. Jeong, et al., Anal. Chem. 92 (2020) 4917-4925;
(e) J.J. Lee, Y.S. Kim, E. Nam, et al., Dalton Trans. 45 (2016) 5700-5712;
(f) Y. Liu, M. Chen, T. Cao, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (2013) 9869-9876;
(g) Z. Guo, W. Zhu, L. Shen, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46 (2007) 5549-5553;
(h) J. Du, J. Fan, X. Peng, et al., Org. Lett. 12 (2010) 476-479;
(i) Y. Zhang, W. Shi, D. Feng, et al., Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 153 (2011) 261-265;
(j) A. CosKun, E.U. Akkaya, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 (2006) 14474-14475;
(k) E.M. Nolan, S.J. Lippard, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125 (2003) 14270-14271;
(l) X. Zhang, Y. Xiao, X. Qian, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47 (2008) 8025-8029;
(m) G. Feng, Y. Ding, Z. Gong, et al., Anal. Sci. 29 (2013) 735-740;
(n) L. Tang, H. Yu, K. Zhong, et al., RSC Adv. 9 (2019) 23316-23323.

 Login In
Login In






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: