pH-Responsive supramolecular DOX-dimer based on cucurbit[8]uril for selective drug release
-
* Corresponding author.
E-mail address: rwang@um.edu.mo (R. Wang).
1 These authors contributed equally to this work.
Citation:
Cheng Qian, Li Shengke, Ma Yanlong, Yin Hang, Wang Ruibing. pH-Responsive supramolecular DOX-dimer based on cucurbit[8]uril for selective drug release[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters,
;2020, 31(5): 1235-1238.
doi:
10.1016/j.cclet.2019.10.020

Chemotherapy, as one of the most common modalities to treat various diseases, such as cancers and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), faces a variety of challenges in clinical applications, including but not limited to poor specificity and associated sideeffects. To address these challenges, a plethora of stimuliresponsive prodrugs including dimeric and polymeric prodrugs have been developed and exhibited therapeutic improvements in preclinical and even clinical settings [1-8]. For instance, camptothecin (CPT) dimer, connected by a reduction-labile maleimide thioether bond was designed and loaded into an acid-active nanoplatform for the targeted killing of tumor cells [9]. Moreover, the CPT dimer possesses Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) effect between CPT and maleimide thioether bond, and the reversion of the dimer to monomeric CPT resulted in the "turnoff" of the FRET signal, making the drug release process trackable. Furthermore, abacavir dimeric prodrug was designed to facilitate the blood brain barrier penetration via inhibiting the drug's efflux by P-glycoprotein, and the dimeric drug was reverted back into potent monomeric therapeutic agent specifically inside target cells [10]. Although these covalent dimeric prodrugs exhibited promising selectivity towards cancer cells, the preparation of these materials often involves ingenious design and complex synthesis, and each synthetic strategy cannot be translated to dimerization of other drug systems. In addition, many of these dimeric prodrugs often need to be further loaded into nanomaterials for improved therapy [2]. A more facile, general approach to prepare dimeric prodrug that may be used directly as a therapeutic agent is highly sought after.
Due to excellent guest-binding behaviours, macrocyclic cucurbit[n]uril (CB[n], n = 5–8 and 10) have attracted increasing attentions in supramolecular chemistry during recent years [11-18]. Recent studies have demonstrated that CB[7] may serve as an effective pharmaceutical excipient that offers a variety of benefits, such as taste-masking and side effect alleviation of the included drugs [19, 20]. On the other hand, CB[8] (Fig. 1) may simultaneously bind two guest drug molecules inside the cavity to form a stable ternary complex, doubling drug loading of that from either CB[7] or CB[8]-based binary complex systems [21-23]. Therefore, CB[8] has been frequently employed as a non-covalent crosslinker in construction of a variety of functional materials [11, 24-28]. One typical example is that peptides or proteins with tryptophan (Trp) or phenylalanine (Phe) residues at N-terminal could be dimerized by CB[8] via homo-ternary complexation, which was firstly discovered by Urbach and coworkers [23]. Such strategy has been applied to dimerize proteins and manipulate their enzymatic activity [29, 30]. Under the same principles, Scherman and co-workers demonstrated the preparation of supramolecular hydrogels by CB[8]-mediated crosslinking of Phe-functionalized polysaccharides, which have exhibited potential applications in controlled drug delivery and tissue engineering [31-33]. Similarly, Wang et al. reported an ecofriendly antibiotic based on CB[8] crosslinked Phe-functionalized polyethylenimine [34]. However, in all of these previous examples, CB[8] was employed to crosslink peptides, proteins and polymers, whereas CB[8]-crosslinked dimeric drug molecules are extremely rare. Herein we designed a doxorubicin (DOX) prodrug DOX-Trp that contains an acid-labile hydrazone bond, and we demonstrate for the first time that a supramolecular dimer of DOX based on CB[8] and Trp modified DOX (DOX-Trp) may act as a stimuli pHresponsive DOX dimer prodrug system that may transport DOX efficiently and selectively to cancer cells. This novel supramolecular drug dimer system resulted in improved therapeutic effect towards cancer cells with minimal cytotoxicity against noncancerous cells.
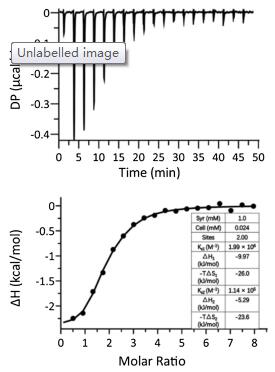
Firstly, Trp conjugated DOX via a hydrazone bond, DOX-Trp was synthesized. The synthetic procedures are detailed in Scheme S1 (Supporting information), and its chemical structure was confirmed by 1H NMR and 13C NMR and HR-ESI-MS. Supramolecular dimer of DOX, crosslinked by CB[8], was formed when DOX-Trp and CB[8] were mixed at 2:1 molecular ratio in an aqueous solution. 1H NMR, isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) and ESI-MS were employed to investigate the formation of such a ternary complex. As shown in Fig. S1 (Supporting information), the mixture exhibited significant exchange broadening on 1H NMR spectra during titration with CB[8], consistent with previous observations reported by Urbach and coworkers, which is inconclusive for the interaction and binding ratio between CB[8] and DOX-Trp [23]. The ITC experiment was conducted by injection of DOX-Trp (1.0 mmol/L) into CB[8] solution (0.024mmol/L) in the cell. The integrated thermogram (Fig. 2) performed after the deduction of the blank control was fitted to the "sequentialbinding"model, resultingina2:1binding stoichiometryof DOX-Trp@CB[8], with stepwise bimolecular association constants determined to be Ks1 = 1.99×106 L/mol and Ks2 = 1.14×105 L/mol, respectively, slightly larger than the previously reported values (Ks1 = 1.3×105 L/mol and Ks2 = 2.8×104 L/mol), likely due to the absenceof saltsin theultrapurewater solutionsinour study, instead of PBS used in the previous study [23, 35]. Furthermore, ESI-MS analysis (Fig. S2 in Supporting information) revealed a characteristic triply charged peak at m/z 939.67, corresponding to [(DOXTrp)2@CB[8]+3H]3+ (calcd. value 939.66), further supported the 2:1 binding ratio between DOX-Trp and CB[8].
As the prodrug DOX-Trp contained an acid-labile hydrazone bond, it was expected that the dimer system would exhibit pH responsive release of DOX under acidic conditions typically encountered in tumour tissues and cells. As the typical pH in cancer tissues and around cancer cells is approximately 6.5 and even lower in lysosome (pH 5.0), and the pH of extracellular fluids and around normal cells is approximately 7.0 [36-38]. Therefore, we chose pH 5.0, 6.5 and 7.0 to examine the drug release behaviours of DOX-Trp@CB[8]. Thus, DOX release rate of the supramolecular dimer was studied under different pH conditions using HPLC. As shown in Fig. 3, the dimer system showed decent stability when incubated in a PBS solution at pH 7.0, with accumulated DOX release less than 16% after incubation for 72 h. Conversely, the release of free DOX reached up to 62% and 49% when incubated at pH 5.0 and 6.5, respectively, for 72 h, confirming the pH sensitivity of the dimer system.
Next, the cellular uptake behaviours of the dimer system by LO2 and BEL 7402 cell lines, as representative noncancerous and cancer cell lines, were investigated via confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) upon incubating the cells with the dimer system for 24 h. As shown in Fig. 4, DAPI was employed to stain the cell nucleus with blue fluorescence, while DOX possesses naturally-occurring red fluorescence. Upon incubation of the cells with DOX-Trp@CB[8] for 24 h, BEL 7402 and LO2 cells exhibited obviously different levels of uptake of DOX, as much higher-intensity of red fluorescence was observed in BEL 7402 cells than that in LO2 cells. In addition, most of red fluorescence in LO2 cells was concentrated in the cytoplasm, while in BEL 7402 cells red fluorescence was mainly situated in the nucleus, suggesting that DOX was effectively released by the dimer system and more efficiently taken up by the cancer cells. With regards to free DOX-Trp (Fig. S3 in Supporting information), both LO2 cells and BEL 7402 cells were infiltrated by red fluorescence produced by DOX, indicating that DOX-Trp does not have the ability to selectively release DOX. In contrast, the dimer system likely remained its integrity in the relatively neutral microenvironment of LO2 cell lines, which has limited its uptake by the cells. Subsequently, the quantitative analysis of cellular uptake by flow cytometry was conducted. As shown in Figs. S4 and S5 (Supporting information), the amount of DOX taken up by BEL 7402 cells was nearly 10-fold higher than that by LO2 cells. This was likely attributed to the different pH micro-environments of cancerous cells and noncancerous cells, where free DOX could not be released at neutral pH conditions encountered near noncancerous cells, resulting in significantly reduced uptake by noncancerous cells.
To further investigate the selective drug release profile of the supramolecular dimer system in cancer cells, cytotoxicity experiment was conducted in both cancerous and non-cancerous cell lines. For comparison, each cell line was incubated with free DOX, DOX-Trp, DOX-Trp@CB[8] and CB[8], respectively, and were subsequently investigated via MTT assays. As shown in Fig. 5, after incubation for 48 h, free DOX, DOX-Trp and DOX-Trp@CB[8] exhibited comparable anticancer activities against BEL 7402 cells with the IC50 (inhibitory concentration to produce 50% cell death) values determined to be 4.85±1.28 μmol/L, 7.168±1.23 μmol/L and 4.61±1.01 μmol/L, respectively. In contrast, the DOX-Trp@CB[8] group exhibited remarkably reduced cytotoxicity against LO2 cell line after 48 h of incubation, when compared to DOX-Trp group and free DOX group. The IC50 value was determined to be 13.66± 1.21 μmol/LforDOX-Trp@CB[8], significantly higher than thatoffree DOX (2.11±1.08 μmol/L) and DOX-Trp (8.01±0.88 μmol/L) against LO2 cells, suggesting that the dimer system may set the ammunition (DOX) free at the target site due to the inherent pH sensitivity. The dramatically improved safety profile of the dimer system against noncancerous cells was consistent with the reduced cellular uptake by noncancerous cells, likely attributed to the reduced transmembrane transport of the supramolecular dimer. Our previous studies have exhibited that supramolecular complexation of a guest species by cucurbituril may inhibit its cellular uptake [39, 40]. In fact, DOX has proven anticancer activity, however, its clinical application has been mainly hampered by its systemic toxicity. Thus, the supramolecular dimer system may provide a novel approach to alleviate the cytotoxicity of DOX while maintaining its cytotoxicity against cancer cells in a specific manner.
In summary, we have designed and developed a novel pHsensitive supramolecular DOX dimer system, via CB[8] mediated DOX-Trp homo-dimerization, which has exhibited selective ammunition (DOX) release in cancer cells, thus exerting a significantly improved safety profile against normal cells while maintaining effective cytotoxicity against cancer cells. Under this strategy, many other anticancer drugs could be chemically modified and loaded as a dimeric "ammunition" into this supramolecular dimer system for improved cancer therapy.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (No. 030/2017/A1), University of Macau (No. MYRG2016-00008-ICMS-QRCM) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21871301).
Supplementary material related to this article canbefound, in the online version, at doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.10.020.
A.G. Cheetham, R.W. Chakroun, W. Ma, H. Cui, Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(2017) 6638-6663.
doi: 10.1039/C7CS00521K
F. Seidi, R. Jenjob, D. Crespy, Chem. Rev. 118(2018) 3965-4036.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00006
X. Pang, Y. Jiang, Q. Xiao, et al., J. Control. Release 222(2016) 116-129.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.024
J. Li, P. Liu, Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 36(2019) 1900113.
doi: 10.1002/ppsc.201900113
Q. Song, X. Wang, Y. Wang, et al., Mol. Pharmaceutics 13(2016) 190-201.
doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00631
Q. Pei, X. Hu, S. Liu, et al., J. Control. Release 254(2017) 23-33.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.03.391
H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Y. Chen, et al., Int. J. Pharm. 549(2018) 230-238.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.07.061
Q. Pei, X. Hu, J. Zhou, S. Liu, Z. Xie, Biomater. Sci. 5(2017) 1517-1521.
doi: 10.1039/C7BM00052A
X. Guo, L. Wang, K. Duval, et al., Adv. Mat. 30(2018) 1705436.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201705436
H.A. Namanja, D. Emmert, D.A. Davis, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc.134(2012) 2976-2980.
doi: 10.1021/ja206867t
S.J. Barrow, S. Kasera, M.J. Rowland, J. del Barrio, O.A. Scherman, Chem. Rev.115(2015) 12320-12406.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00341
K.I. Assaf, W.M. Nau, Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(2015) 394-418.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00273C
D. Shetty, J.K. Khedkar, K.M. Park, K. Kim, Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(2015) 8747-8761.
doi: 10.1039/C5CS00631G
N. Song, X.Y. Lou, L. Ma, H. Gao, Y.W. Yang, Theranostics 9(2019) 3075-3093.
doi: 10.7150/thno.31858
J. Zhou, G. Yu, F. Huang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(2017) 7021-7053.
doi: 10.1039/C6CS00898D
X.Y. Hu, L. Gao, S. Mosel, et al., Small 14(2018) 1803952.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201803952
Y.Chen, Z.Huang, H.Zhao, etal., ACSAppl.Mater.Interfaces9(2017)8602-8608.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b01157
J. Tian, C. Yao, W.L. Yang, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 28(2017) 798-806.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.01.010
X. Yang, S. Li, Q.W. Zhang, et al., Nanoscale 9(2017) 10606-10609.
doi: 10.1039/C7NR03608F
Q. Huang, S. Li, H. Yin, et al., Food Chem. Toxicol. 112(2018) 421-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.12.016
H.J. Kim, J. Heo, W.S. Jeon, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40(2001) 1526-1529.
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20010417)40:8<1526::AID-ANIE1526>3.0.CO;2-T
M.E. Bush, N.D. Bouley, A.R. Urbach, J. Am. Chem. Soc.127(2005) 14511-14517.
doi: 10.1021/ja0548440
L.M. Heitmann, A.B. Taylor, P.J. Hart, A.R. Urbach, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128(2006) 12574-12581.
doi: 10.1021/ja064323s
S.K. Samanta, D. Moncelet, V. Briken, L. Isaacs, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138(2016) 14488-14496.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b09504
Y. Wang, D. Li, H. Wang, et al., Chem. Commun. 50(2014) 9390-9392.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC03978E
Y. Yang, H. Hu, L. Chen, et al., Mater. Chem. Front. 3(2019) 806-811.
doi: 10.1039/C9QM00028C
J. Tian, T.Y. Zhou, S.C. Zhang, et al., Nat. Commun. 5(2014) 5574.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6574
Z. Huang, L. Yang, Y. Liu, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53(2014) 5351-5355.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201402817
P.J. de Vink, J.M. Briels, T. Schrader, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56(2017) 8998-9002.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201701807
R.P.G. Bosmans, J.M. Briels, L.G. Milroy, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55(2016) 8899-8903.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201602807
C. Li, M.J. Rowland, Y. Shao, et al., Adv. Mat. 27(2015) 3298-3304.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201501102
M.J. Rowland, C.C. Parkins, J.H. McAbee, et al., Biomaterials 179(2018) 199-208.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.05.054
M.J. Rowland, M. Atgie, D. Hoogland, O.A. Scherman, Biomacromolecules 16(2015) 2436-2443.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00680
S. Li, N. Jiang, W. Zhao, et al., Chem. Commun. 53(2017) 5870-5873.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC02466E
W. Ong, A.E. Kaifer, J. Org. Chem. 69(2004) 1383-1385.
doi: 10.1021/jo035030+
P.P. Hsu, D.M. Sabatini, Cell 134(2008) 703-707.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.021
Y. Liu, W. Wang, J. Yang, C. Zhou, J. Sun, Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 8(2013) 159-167.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2013.07.021
C. Gao, F. Tang, G. Gong, et al., Nanoscale 9(2017) 12533-12542.
doi: 10.1039/C7NR03611F
X. Zhang, Q. Huang, Z.Z. Zhao, et al., J. Agr. Food Chem. 67(2019) 7783-7792.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00764
X. Zhang, X. Xu, S. Li, et al., Theranostics 9(2019) 633-645.
doi: 10.7150/thno.31485
A.G. Cheetham, R.W. Chakroun, W. Ma, H. Cui, Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(2017) 6638-6663.
doi: 10.1039/C7CS00521K
F. Seidi, R. Jenjob, D. Crespy, Chem. Rev. 118(2018) 3965-4036.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00006
X. Pang, Y. Jiang, Q. Xiao, et al., J. Control. Release 222(2016) 116-129.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.024
J. Li, P. Liu, Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 36(2019) 1900113.
doi: 10.1002/ppsc.201900113
Q. Song, X. Wang, Y. Wang, et al., Mol. Pharmaceutics 13(2016) 190-201.
doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00631
Q. Pei, X. Hu, S. Liu, et al., J. Control. Release 254(2017) 23-33.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.03.391
H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Y. Chen, et al., Int. J. Pharm. 549(2018) 230-238.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.07.061
Q. Pei, X. Hu, J. Zhou, S. Liu, Z. Xie, Biomater. Sci. 5(2017) 1517-1521.
doi: 10.1039/C7BM00052A
X. Guo, L. Wang, K. Duval, et al., Adv. Mat. 30(2018) 1705436.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201705436
H.A. Namanja, D. Emmert, D.A. Davis, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc.134(2012) 2976-2980.
doi: 10.1021/ja206867t
S.J. Barrow, S. Kasera, M.J. Rowland, J. del Barrio, O.A. Scherman, Chem. Rev.115(2015) 12320-12406.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00341
K.I. Assaf, W.M. Nau, Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(2015) 394-418.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00273C
D. Shetty, J.K. Khedkar, K.M. Park, K. Kim, Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(2015) 8747-8761.
doi: 10.1039/C5CS00631G
N. Song, X.Y. Lou, L. Ma, H. Gao, Y.W. Yang, Theranostics 9(2019) 3075-3093.
doi: 10.7150/thno.31858
J. Zhou, G. Yu, F. Huang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(2017) 7021-7053.
doi: 10.1039/C6CS00898D
X.Y. Hu, L. Gao, S. Mosel, et al., Small 14(2018) 1803952.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201803952
Y.Chen, Z.Huang, H.Zhao, etal., ACSAppl.Mater.Interfaces9(2017)8602-8608.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b01157
J. Tian, C. Yao, W.L. Yang, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 28(2017) 798-806.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.01.010
X. Yang, S. Li, Q.W. Zhang, et al., Nanoscale 9(2017) 10606-10609.
doi: 10.1039/C7NR03608F
Q. Huang, S. Li, H. Yin, et al., Food Chem. Toxicol. 112(2018) 421-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.12.016
H.J. Kim, J. Heo, W.S. Jeon, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40(2001) 1526-1529.
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20010417)40:8<1526::AID-ANIE1526>3.0.CO;2-T
M.E. Bush, N.D. Bouley, A.R. Urbach, J. Am. Chem. Soc.127(2005) 14511-14517.
doi: 10.1021/ja0548440
L.M. Heitmann, A.B. Taylor, P.J. Hart, A.R. Urbach, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128(2006) 12574-12581.
doi: 10.1021/ja064323s
S.K. Samanta, D. Moncelet, V. Briken, L. Isaacs, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138(2016) 14488-14496.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b09504
Y. Wang, D. Li, H. Wang, et al., Chem. Commun. 50(2014) 9390-9392.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC03978E
Y. Yang, H. Hu, L. Chen, et al., Mater. Chem. Front. 3(2019) 806-811.
doi: 10.1039/C9QM00028C
J. Tian, T.Y. Zhou, S.C. Zhang, et al., Nat. Commun. 5(2014) 5574.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6574
Z. Huang, L. Yang, Y. Liu, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53(2014) 5351-5355.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201402817
P.J. de Vink, J.M. Briels, T. Schrader, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56(2017) 8998-9002.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201701807
R.P.G. Bosmans, J.M. Briels, L.G. Milroy, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55(2016) 8899-8903.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201602807
C. Li, M.J. Rowland, Y. Shao, et al., Adv. Mat. 27(2015) 3298-3304.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201501102
M.J. Rowland, C.C. Parkins, J.H. McAbee, et al., Biomaterials 179(2018) 199-208.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.05.054
M.J. Rowland, M. Atgie, D. Hoogland, O.A. Scherman, Biomacromolecules 16(2015) 2436-2443.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00680
S. Li, N. Jiang, W. Zhao, et al., Chem. Commun. 53(2017) 5870-5873.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC02466E
W. Ong, A.E. Kaifer, J. Org. Chem. 69(2004) 1383-1385.
doi: 10.1021/jo035030+
P.P. Hsu, D.M. Sabatini, Cell 134(2008) 703-707.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.021
Y. Liu, W. Wang, J. Yang, C. Zhou, J. Sun, Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 8(2013) 159-167.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2013.07.021
C. Gao, F. Tang, G. Gong, et al., Nanoscale 9(2017) 12533-12542.
doi: 10.1039/C7NR03611F
X. Zhang, Q. Huang, Z.Z. Zhao, et al., J. Agr. Food Chem. 67(2019) 7783-7792.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00764
X. Zhang, X. Xu, S. Li, et al., Theranostics 9(2019) 633-645.
doi: 10.7150/thno.31485

Linghui Zou , Meng Cheng , Kaili Hu , Jianfang Feng , Liangxing Tu . Vesicular drug delivery systems for oral absorption enhancement. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(7): 109129-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109129
Yunkang Tong , Haiqiao Huang , Haolan Li , Mingle Li , Wen Sun , Jianjun Du , Jiangli Fan , Lei Wang , Bin Liu , Xiaoqiang Chen , Xiaojun Peng . Cooperative bond scission by HRP/H2O2 for targeted prodrug activation. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(12): 109663-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109663
Zhilong Xie , Guohui Zhang , Ya Meng , Yefei Tong , Jian Deng , Honghui Li , Qingqing Ma , Shisong Han , Wenjun Ni . A natural nano-platform: Advances in drug delivery system with recombinant high-density lipoprotein. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(11): 109584-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109584
Yong-Dan Zhao , Yidan Wang , Rongrong Wang , Lina Chen , Hengtong Zuo , Xi Wang , Jihong Qiang , Geng Wang , Qingxia Li , Canqi Ping , Shuqiu Zhang , Hao Wang . Reversing artemisinin resistance by leveraging thermo-responsive nanoplatform to downregulating GSH. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(6): 108929-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108929
Xingqun Pu , Rongrong Liu , Yuting Xie , Chenjing Yang , Jingyi Chen , Baoling Guo , Chun-Xia Zhao , Peng Zhao , Jian Ruan , Fangfu Ye , David A Weitz , Dong Chen . One-step preparation of biocompatible amphiphilic dimer nanoparticles with tunable particle morphology and surface property for interface stabilization and drug delivery. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(3): 109820-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109820
Makhloufi Zoulikha , Zhongjian Chen , Jun Wu , Wei He . Approved delivery strategies for biopharmaceuticals. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(2): 110225-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110225
Jing Zhang , Charles Wang , Yaoyao Zhang , Haining Xia , Yujuan Wang , Kun Ma , Junfeng Wang . Application of magnetotactic bacteria as engineering microrobots: Higher delivery efficiency of antitumor medicine. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(10): 109420-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109420
Tong Tong , Lezong Chen , Siying Wu , Zhong Cao , Yuanbin Song , Jun Wu . Establishment of a leucine-based poly(ester amide)s library with self-anticancer effect as nano-drug carrier for colorectal cancer treatment. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(12): 109689-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109689
Jiaqi Huang , Renjiang Kong , Yanmei Li , Ni Yan , Yeyang Wu , Ziwen Qiu , Zhenming Lu , Xiaona Rao , Shiying Li , Hong Cheng . Feedback enhanced tumor targeting delivery of albumin-based nanomedicine to amplify photodynamic therapy by regulating AMPK signaling and inhibiting GSTs. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(8): 109254-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109254
Lihang Wang , Mary Li Javier , Chunshan Luo , Tingsheng Lu , Shudan Yao , Bing Qiu , Yun Wang , Yunfeng Lin . Research advances of tetrahedral framework nucleic acid-based systems in biomedicine. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(11): 109591-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109591
Keyang Li , Yanan Wang , Yatao Xu , Guohua Shi , Sixian Wei , Xue Zhang , Baomei Zhang , Qiang Jia , Huanhua Xu , Liangmin Yu , Jun Wu , Zhiyu He . Flash nanocomplexation (FNC): A new microvolume mixing method for nanomedicine formulation. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(10): 109511-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109511
Yuanzheng Wang , Chen Zhang , Shuyan Han , Xiaoli Kong , Changyun Quan , Jun Wu , Wei Zhang . Cancer cell membrane camouflaged biomimetic gelatin-based nanogel for tumor inhibition. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(11): 109578-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109578
Yinglan Yu , Sajid Hussain , Jianping Qi , Lei Luo , Xuemei Zhang . Mechanisms and applications: Cargos transport to basolateral membranes in polarized epithelial cells. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(12): 109673-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109673
Han Wu , Yumei Wang , Zekai Ren , Hailin Cong , Youqing Shen , Bing Yu . The nanocarrier strategy for crossing the blood-brain barrier in glioma therapy. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(4): 109996-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109996
Mengwei Ye , Qingqing Xu , Huanhuan Jian , Yiduo Ding , Wenpeng Zhao , Chenxiao Wang , Junya Lu , Shuaipeng Feng , Siling Wang , Qinfu Zhao . Recent trends of biodegradable mesoporous silica based nanoplatforms for enhanced tumor theranostics. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(6): 110221-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110221
Jie Yang , Xin-Yue Lou , Dihua Dai , Jingwei Shi , Ying-Wei Yang . Desymmetrized pillar[8]arenes: High-yield synthesis, functionalization, and host-guest chemistry. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(1): 109818-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109818
Yunjie Dang , Yanru Feng , Xiao Chen , Chaoxing He , Shujie Wei , Dingyang Liu , Jinlong Qi , Huaxing Zhang , Shaokun Yang , Zhiyun Niu , Bai Xiang . Development of a multi-level pH-responsive lipid nanoplatform for efficient co-delivery of siRNA and small-molecule drugs in tumor treatment. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(12): 109660-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109660
Li Fu , Ziye Su , Shuyang Wu , Yanfen Cheng , Chuan Hu , Jinming Zhang . Redox-responsive hyaluronic acid-celastrol prodrug micelles with glycyrrhetinic acid co-delivery for tumor combination therapy. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(5): 110227-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110227
Xianchen Hu , Junli Yang , Fang Gao , Zhiyong Zhao , Simin Liu . Highly selective [4+4] cross-photodimerization of (4a-azonia)anthracenes driven by confinement of D-A hetero-guest pair in cucurbit[10]uril host. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(3): 109967-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109967
Shaojie Deng , Peihua Ma , Qinghong Bai , Xin Xiao . The transformation of nor-seco-cucurbit[10]uril to cucurbit[5]uril and cucurbit[8]uril controlled by its own concentration. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(2): 109878-. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109878